week10报告
所有相关文件可以在 这里 找到。
所有图片中的内容,包括代码、控制台输出,均可以在该文档中找到。
题目列表
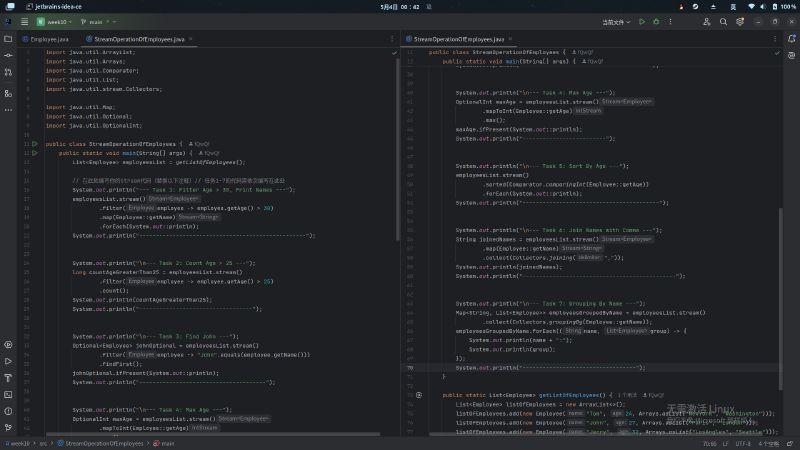
- 过滤与映射
给定员工列表,找出所有年龄大于30岁的员工,并打印他们的姓名。
示例输出:Jerry - 计数操作
统计年龄大于25岁的员工数量。
示例输出:3 - 查找操作
找到名为“John”的员工并打印其信息。
示例输出:Employee [name=John, age=27] - 最大值操作
找出所有员工中的最大年龄。
示例输出:32 - 排序操作
将员工列表按年龄升序排序,并打印排序后的结果。
示例输出:1 2 3Employee [name=Amit, age=22] Employee [name=Tom, age=24] ...(其他员工) - 字符串归约
将所有员工的姓名用逗号连接成一个字符串。
示例输出:Tom,John,Jerry,Amit,Amit - 分组操作
将员工按姓名分组,并按格式打印结果:1 2 3 4 5John: [Employee [name=John, age=27]] Amit: [Employee [name=Amit, age=22], Employee [name=Amit, age=24]] ...(其他分组)
作答
| |
控制台输出
| |
总结
本次作业实践了Java Stream API在处理集合数据时的常用操作。关键点包括:
- 链式调用: 将多个操作(如 filter, map, sorted)串联起来,代码简洁易读。
- 中间操作: filter, map, sorted 等,用于转换或筛选流,返回新的流。
- 终端操作: forEach, count, max, findFirst, collect 等,用于触发计算并产生最终结果或副作用。
- Lambda表达式/方法引用: 大量用于定义操作逻辑,体现了函数式编程风格。
- Collectors: Collectors.joining 和 Collectors.groupingBy 展示了强大的数据汇总和分组能力。
总的来说,Stream API提供了一种更高效的方式来处理集合,减少了传统的迭代和条件判断样板代码。